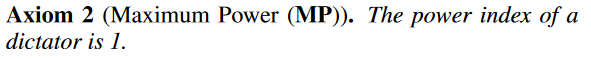Meeting - 10th May 2022
Meeting 2 of DAO Governance Literature Review - 10th May 2022
Attendees
Amar Khan | |
Kenric Nelson | Photrek |
Philip Lazos | IOG |
Stephen Whitenstall | QADAO |
Steph Macurdy | Wolfram Blockchain Labs |
Information
Community Governance Group
https://quality-assurance-dao.gitbook.io/community-governance-oversight/
Meeting GitHub Task
https://github.com/Catalyst-Auditing/Community-Governance-Oversight-Coordination/issues/71
Overview
After preliminary Zotero housekeeping, discussion moved onto Liquid Democracy papers.
Context
For context the papers we're looking at is background for D reps. Papers that are relevant to liquid democracy and in the context of IOGs implementation of D reps. - Stephen
Particularly methodologies for measuring power in these kinds of voting systems. - Kenric
I'm not necessarily looking for this literature review to provide answers. But rather to help provide some guidance to the community about what the important questions are on these issues. And in defining good questions, I'm hoping to kind of motivate research and development within the community to try to tackle some of these questions. - Kenric
And the other contextual point is that this is part of an effort by Governance Oversight to do surveys within the community. A survey of the literature as a way to inform a more in depth conversation with the community and with IOG, with regard to the designs, and expectations we should have about the outcomes of the direct process. - Kenric
Community Governance Oversight is a proposal that was submitted to Project Catalyst. It was jointly prepared with the community, IOG, Dor and Harris to oversee governance processes. It was funded in Fund 7, it may be funded in Fund 8. Part of that is to oversee D reps, Catalyst Circle Problem Sensing and Challenge Setting. - Stephen
Review of "Power in Liquid Democracy"
What I'd like to do is use the tags to put our names so that we have a record of who provided the entry. So on your note, if you can add a tag with your name, that will be helpful. - Kenric
Brief Summary
The paper develops a theory of power for delegable proxy voting systems.
It defines a power index to measure the influence of voters and delegators.
A formal theory of power with a delegated proxy was lacking.
So the aim was to provide a theory to gain insight into how power may have been to be distributed among agents.
The authors analytically study the existence of pure strategy Nash equilibrium.
What does Nash equilibrium mean? Nash equilibrium is the most common way to define the solution of a non cooperative game involving two or more players. Each player is assumed to know the equilibria rooms, strategies of other players, and no one has anything to gain by changing only one's own strategy.
I think that might be helpful for just explaining what's the the importance of Nash equilibrium? - Steph
See also Steph's Notes below
Portfolio allocation of voting power
One of my immediate first thoughts was if people are delegating votes are we going to have a portfolio? Are we going to get to a point similar to how you allocate your financial portfolio? Are you going to do a portfolio allocation of voting power?
If I have 100 votes am I going to be able to choose a little bit here or allocate a little bit there ? - Steph
28:41
From what IOG has communicated that is the intent. They haven't rolled it out yet. But part of the idea behind liquid democracy and the plans for the delegated reps is that you wouldn't necessarily delegate all your power to one representative, but you might spread that power across several representatives. - Kenric
Researching dRep's background
I envision a research report that says this delegate rep is experienced in a particular area. There is evidence of what they understand and their previous voting record.
This is their Wallet account. This is what they currently hold. This is how long they've been participating.
And instead of me knowing about those things intimately it is enough that I just I need to know the reputation of somebody.
And if I feel strongly about it, then I'm 50% allocated to them. And if I just want to make sure I hedge myself, I'm 10% to the opposite extreme.
In the paper, they reference something called Liquid feedback. A website called liquid feed. - Steph
Liquid Feedback - https://liquidfeedback.com/en/
Liquid Feedback
Liquid feedback brought up the idea of favoring preferences and giving somebody the option of having a secondary choice. And where, as opposed to only having all all on one vote, it's, you do have the ability to represent secondary, and third choices. - Steph
Transitive delegations
One main starting point of our paper is a controversial feature of liquid democracy. That is, transitive delegations may, in principle, lead to disproportionate accrual of power, thereby harming the democratic legitimacy of the resulting vote.
Kenric, this is a thing that you focus on a lot. - Steph
Banzhaf power index
The Banzhaf power index is a power index, defined by the probability of changing an outcome of a vote where voting rights are not necessarily equally divided among the vote, voters or shareholders. - Steph
Definition of terms
The authors define seven different elements of these games, I'll just go through a couple of them. - Kenric
Dummy agent
They define for instance, a dummy agent, which is an individual in the system, who has no influence on the outcomes of decisions. So whatever coalition they join into and making a choice, it doesn't change the outcome of that coalition of the coalition's vote. - Kenric
Dictator
And then on the other extreme, is a dictator, who, whichever coalition he decides to join, becomes the winning coalition. - Kenric
Block Formation
And then, there's other things in here, including the ability to kind of compose both games and the effect of agents.
So like a block formation is when, what two or more agents combined to form one block vote. And then composition has to do with rules around how if you find sort of two separate games, how do those games end up being combined?
Axioms
Now those definitions are used to form a set of axioms. And again, there's sort of a connection with this.
So the first axiom is defining the fact that you have no power, which would be the dummy agent.
The second axiom is defining the maximum power. And it's a scale between zero and one.
And then again, there's some rules around how power is combined in the system. With regard to blocks and a sum principle. I won't go into the details of that now.
But it leads to then a characterization of these games.
And this definition of voting power, where he has two levels, one lemma is that this delegated and another which defines a power index. - Kenric
Concluding Theorem - Banzhaf power index
The authors conclude with the theorem that the power index for liquid democracy satisfies all five axioms, if and only if it is this delegated Banzhaf index.
So, the main result of the paper is a proof that this particular way of measuring power in a delegated liquid democracy system is the only power index that satisfies these five axioms. - Kenric
What is the Banzhaf power index ?
The probability of changing an outcome of a vote where voting rights are not necessarily equally divided among the voters or shareholders. - Stephen
What is the main takeaway ?
I'd be curious, just how would we think about presenting this to the larger Catalyst or Cardano community as functional input?
What's the main takeaway here? Because at the end the purpose is to inform the community and be able to get urvey results. - Steph
Summary of DAO Literature Review Plan
The plan is to take these notes that each of us gather about different papers, and put it into one document that will give the full reference for the paper and a hyperlink to where people can find it and our summary of that paper.
This can be the beginning of a resource to help educate the community about what scientists in the field of political systems and political economic systems have been communicating about these types of structures.
This will also inform our work towards thinking about what the proper focus of a good white paper could be that will we'll write as a team. - Kenric
Does this just apply the Banzhaf index to Liquid democracy ?
In summary, does this just apply the Banzhaf index to liquid democracy? Is that all that the paper does? Or does it add something new to the table? - Stephen
References
Kenric's Notes on "Power in Liquid Democracy"
Definitions of DB
Def 1: Dummy Agent - an agent that does not influence any of the coalitions
Def 2: Dictator - nu’_V(C) = 1 only if i is a member of the coalition
Def 3: Symmetric Agent - addition of i or j to a coalition produces the same nu’ (ie winning or losing coalition)
Def 4: Minimally Winning Coalition - removing any member i from coalition C causes transition from winning to losing
Def 5: Unanimity LDE UDLE - The threshold, beta, is equal to the sum of all delegate weights, w(i). Thus unanimity is the only winning coalition
Def 6: Composition - Union and Intersection of two games V_1 and V_2 can be defined by the union or intersection of the components of the games
Def 7: Bloc Formation - agents i and j are joined to represent one new agent ij; repeated application of bloc formation can coalesce all agents who share the same guru
Steph's Notes on "Power in Liquid Democracy"
Steph Macurdy: The paper develops a theory of power for delegable proxy voting systems. We define a power index able to measure the influence of both voters and delegators.
However, a formal theory of power in voting systems with delegable proxy is lacking. We aim at providing such a theory here, and use it to gain insights into how power may happen to be distributed among agents involved in decision-making with liquid democracy
We analytically study the existence of pure strategy Nash equilibria in such a model. Finally, by means of simulations, we study the effect of relevant parameters on the emergence of power inequalities in the model.
Nash equilibrium is the most common way to define the solution of a non-cooperative game involving two or more players. In a Nash equilibrium, each player is assumed to know the equilibrium strategies of the other players, and no one has anything to gain by changing only one's own strategy. (Wikipedia)
Delegable voting gives rise to so-called "transitive delegations."
Can either cast vote directly or delegate, passing votes one has accrued further to another proxy.
Portfolio allocation of votes
Snapshot results of different governance implementations
Liquid Feedback - https://liquidfeedback.com/en/
Favoring preferences and secondary choice.
"The starting point of our paper is a controversial feature of liquid democracy: transitive delegations may in principle lead to disproportionate accrual of power, thereby harming the democratic legitimacy of the resulting vote."
"is a power index defined by the probability of changing an outcome of a vote where voting rights are not necessarily equally divided among the voters or shareholders." - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Banzhaf_power_index)
"Winner take all dynamics when its only one vote per person?"
Banzhaf Power Index
Banzhaf Power Index - Wolfram Demonstrations Project
The Banzhaf index is a measure of how probable it is that someone's vote will change the outcome of an election in settings in which voters may have unequal numbers of votes. This Demonstration examines a scenario with six voters, each of whom have a user selectable number of votes. You can also determine the percentage of total votes needed to win. From this data, the Demonstration shows all the winning coalitions that can form and all the members of each coalition ("the swing voters") who, if they had voted differently, would have changed the outcome of the election. The Banzhaf index, which ranges from 0 to 1, is the percentage of times each voter is a swing voter over all possible winning coalitions.
Last updated